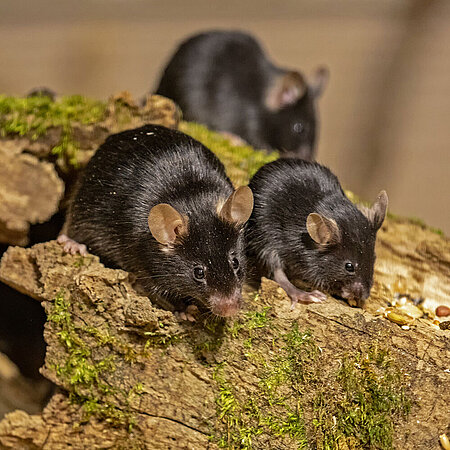
House mouse
Mus musculus

- FamilyLong-tailed mice (Muridae)
- Weightca. 20 – 30 g
- HabitatSteppes and semi-deserts, buildings and storage facilities
Wherever humans go, mice follow
House mice are rodents that live in groups of up to 50 individuals. Originally, they were only adapted to life on the steppes of Central Asia. But with the advent of agriculture and food storage, they followed man and spread with him across the globe. Since then, they have made their burrows not only under rocks and roots, but also in cracks and niches of buildings.

Valuable contribution to science
Laboratory-bred mice are used for research in medicine and other scientifi c disciplines. The little rodent’s ease of maintenance, short reproductive cycle, and extensively researched biology make it the model organism for many areas of human-oriented research. Modern science owes many important biological discoveries to the mouse.
Mice communicate using pheromones in their urine to tell each other who’s in charge, who’s related to whom and who’s ready to mate.
Distribution