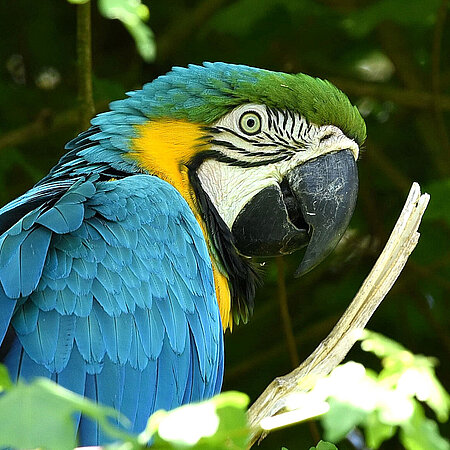
Yellow and Breast Macaw
Ara ararauna

- Family
- Parrots (Psittacidae)
- Weight
- 1.040 – 1.280 g
- Habitat
- subtropical and tropical forests
Antitoxins from the mountains
The rainforest is filled with a wide variety of fruits, nuts and buds, most of which the blue-and-yellow macaw digests well. Occasionally, however, they may consume a poisonous fruit. However the bird has found a way to protect its stomach from such toxic food by eating clay - washed down from the Andes and settled on the river banks - two to three times a week. The clay in the blue-and-yellow macaw’s stomach absorbs the toxins consumed and neutralises them.

Faithful bird
If two blue-and-yellow macaws find each other, they remain together for a lifetime. The pair usually breeds in the same tree cavity, which can be up to 40 m high, for many years. Blue-and-yellow macaws live in relatively large groups. Couples often preen each other, making it easy to identify who belongs to whom in the group.
They fly up to 25 km away from their nesting area to visit their feeding ground.
Distribution