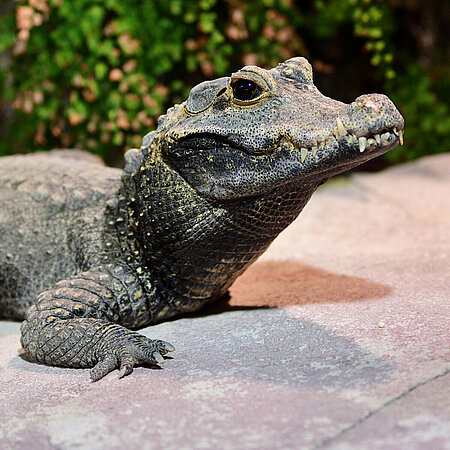
Dwarf crocodile
Osteolaemus tetraspis

- FamilyTrue crocodiles (Crocodylidae)
- Length1,5 – 2,3 m
- HabitatWetlands and swamp forests
Fluctuating body temperature
Crocodiles do not have a constant body temperature but it rises and falls depending on the ambient temperature. If they feel cold, they will bask in the sun. Likewise, they will move into the shade when it gets too hot. Crocs can also cool off by opening their mouth – as the saliva evaporates it carries away some of the animal’s body heat. The dwarf crocodile is perfectly adapted to life in the water. It can shut tight its nostrils and hold its breath for long periods when submerged.
Occasional herbivore
The dwarf crocodile hunts at dusk and at night. Its prey consists mainly of fi sh, crustaceans and small vertebrates. Surprisingly, the crocodile also loves fruits to supplement its diet. In times of scarcity, it can survive for months without food.
Biodiversity under threat
Dwarf crocodiles are kept as a living source of food in lean times.
Distribution

Hellabrunn participates in the European Studbook